
29 And God said, Behold, I have given you every herb bearing seed, which is upon the face of all the earth, and every tree, in the which is the fruit of a tree yielding seed; to you it shall be for meat.
30 And to every beast of the earth, and to every fowl of the air, and to every thing that creepeth upon the earth, wherein there is life, I have given every green herb for meat: and it was so.
The bible is clear on what plants are given for…
to you it shall be for meat ( cow, goat ,etc.) for your body but for meat.
Cain ( The vegetarian) Kills Abel ( Meat eater)
Now Abel kept flocks, and Cain worked the soil. 3 In the course of time Cain brought some of the fruits of the soil as an offering to the Lord. 4 And Abel also brought an offering—fat portions from some of the firstborn of his flock. The Lord looked with favor on Abel and his offering, 5 but on Cain and his offering he did not look with favor. So Cain was very angry, and his face was downcast.
In Genesis 1:29-30, the Bible provides a clear directive about the role of plants in our diet and the natural order:
“And God said, Behold, I have given you every herb bearing seed, which is upon the face of all the earth, and every tree, in the which is the fruit of a tree yielding seed; to you it shall be for meat, to every beast of the earth, and to every fowl of the air, and to every thing that creepeth upon the earth, wherein there is life, I have given every green herb for meat: and it was so.”
Genesis 1:29-30
From this passage, it’s evident that plants are intended to be a source of nourishment for both animals, which is your meat or your physical meat body. Thus your body is also animal, so plants shall be eaten, but there are rules. Many Rules that you need to learn.
eg. For there was nice sweet corn and Cain, brought some watermellons and some nice corn to the Gods as an offering and they just watch Cain like if he was an insult to them.
However Abel brought a nice goat or lamb or something, and there was a part a barbecue and those who called themselves the God were happy with Cain.
So Cain Killed Abel – why? Why didn’t Cain just start to take care of some goats or sheep, cows, dear etc. Why just kill Able.
Well this is what happened, Cain and Able were given these task by those so named the gods.( not the creator, the creator don’t enforce nothing on free souls). These gods came and told Cain he has to grown these specific vegetable and were to supply them to Abel for the Animals. It was a chain of manufacturing,- division of labor and also a sort of way to keep ” the knowledge of the gods” away from one person. See Cain was out in the field toiling to grow the grass and vegetable – not corn or wealth etc. just some wild grass and these were used to feed the animals. These animals were not just grazing openly, they were well taken care off, and at times Abel would take them to the open field of Cain to eat the grass.
However, when it came to the time for presenting the gods with their offering, aka food. Cain had only these grasslands and grass to show, he didn’t understand why he was shunned, and didn’t understand his important in the chain of command. Largely, the reaction of the gods, were Alway in connection of the animals, they were picking and inspecting, seeking out the best of the animals for their parties, their foods. Yes, these gods were mask men, men in mask, imagine having a computer a working cell phone, whatsapp in 2024 and going back in 1700.. yep, you are a god to these people.
So this is where the jealousy came from, a lack of understand by Cain in his role to make the feed for the animals and the lack of the holistic picture. Actually, it is and wants his fault. it was the gods who wanted to separate the process for their own security, trying to ensure that “man” could understand the full process of creating food…
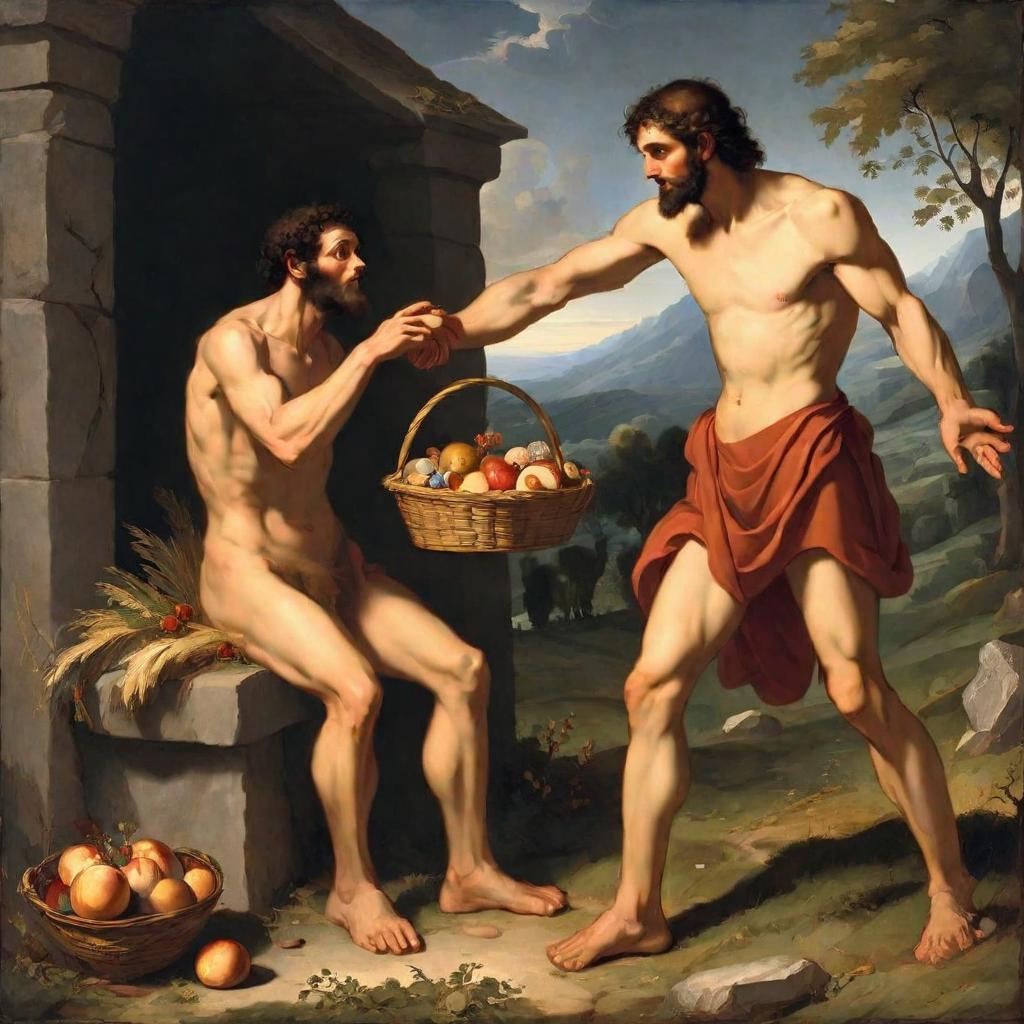

However, a deeper dive into biblical narratives reveals a more complex relationship between diet and divine favor, exemplified in the story of Cain and Abel. Abel, a keeper of flocks, offered fat portions from the firstborn of his flock, while Cain, who worked the soil, brought fruits of the soil as his offering. The gods looked with favor on Abel’s offering but did not look with favor on Cain’s offering, which led to Cain’s anger and ultimately, his tragic decision to kill Abel.
This distinction between the offerings of Cain and Abel raises intriguing questions about the symbolism of meat and plants in the biblical context. Abel’s offering of meat was favored by gods, while Cain’s plant-based offering was not. This narrative suggests a deeper significance to the consumption of meat, aligning it with divine approval.
In essence, while plants are given to us for sustenance, as stated in Genesis, the story of Cain and Abel introduces a nuanced view on the consumption of meat and its perceived value in the eyes of gods. This dichotomy continues to provoke thought and discussion about the spiritual and dietary teachings found within the Bible.
And this is what the Roman pieced up in their study of the literature now called the Vatican. They realized that all these things were not given by the creator but by a strain of men, who were created but were more advanced in knowledge to the people of the day, a set of invaders who has to ultimately leave the earth and return to their place. In this case, the Church – RC – Church realized and siege the opportunity by hiding the knowledge from the public john dow and created a new plan, we the church will be the new gods, we will have people now giving us the offerings of meat, plants, seeds, gold, silver, and all things we need. We will go to the land far away and say to those who live there – we are the new gods – we demand that you obey us.
For none of these are from creator – if you want creator’s story, listen to your SOUL, listen to your self, and this when it is clear will open you to the creators’ universal and individual.
Creators has made us free and full.
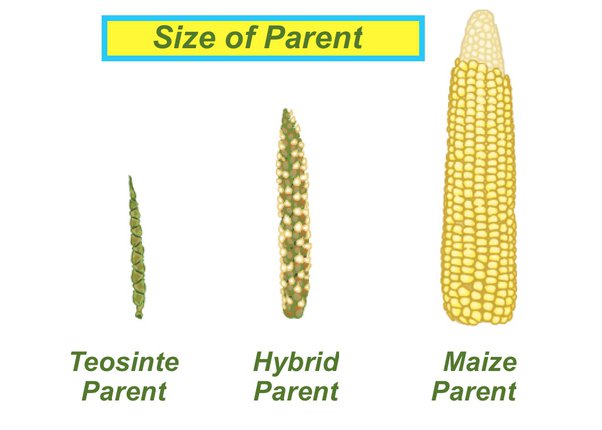
Corn’s origins can be traced to the ancient region of Mesoamerica, which includes parts of modern-day Mexico and Central America. The wild ancestor of corn, teosinte, was a grassy plant with small, hard kernels. Around 9,000 years ago, indigenous peoples in this region began selectively breeding teosinte, eventually transforming it into the larger, more productive ears of corn we recognize today.
GMO Corn – want it always meant for the Cow.
Modern Cultivation
Today, corn is one of the most widely grown crops in the world, used for food, livestock feed, and industrial products. Advances in agricultural science, including hybridization and genetic modification, have further enhanced its productivity and resilience.
The Historical Context of Key Plants
Wheat
Origin: Fertile Crescent (modern-day Middle East)
Historical Context: One of the first crops to be domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Wheat cultivation marked the beginning of agriculture and led to the establishment of permanent settlements and the rise of civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt.
Rice
Origin: Yangtze River Valley, China
Historical Context: Domesticated around 9,000 years ago, rice has been a staple food in Asia for millennia. It supported the growth of major civilizations in China, India, and Southeast Asia and remains a crucial crop globally.
Maize (Corn)
Origin: Mesoamerica (modern-day Mexico)
Historical Context: Domesticated around 9,000 years ago from the wild grass teosinte. It became the foundation of civilizations like the Maya, Aztec, and Inca. After European contact, maize spread globally and is now a key food crop and industrial product.
Barley
Origin: Fertile Crescent
Historical Context: One of the earliest domesticated grains, used for food and brewing beer. Barley was crucial in ancient Mesopotamian, Egyptian, and Greek cultures.
Soybeans
Origin: East Asia (China)
Historical Context: Cultivated for thousands of years, soybeans are a major protein source in Asian diets and have become globally important due to their versatility and use in products like tofu, soy sauce, and animal feed.
Potato
Origin: Andes Mountains, South America
Historical Context: Domesticated around 8,000 years ago by indigenous peoples. The potato became a staple in Europe after its introduction in the 16th century, significantly impacting European agriculture and cuisine.
Cassava (Manioc)
Origin: South America (Amazon Basin)
Historical Context: Domesticated by indigenous peoples of the Amazon. Cassava is a staple food in many tropical regions and is crucial for food security in parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
Tomato
Origin: South America (Andes)
Historical Context: Domesticated by indigenous peoples in the Andes and cultivated by the Aztecs in Mesoamerica. Introduced to Europe in the 16th century, it became a central ingredient in Mediterranean cuisine.
Peanut
Origin: South America (Andes)
Historical Context: Domesticated by indigenous peoples and spread throughout the world after European contact. Peanuts are now a significant crop in many tropical and subtropical regions.
Coffee
Origin: Ethiopia
Historical Context: Discovered by indigenous peoples in Ethiopia, coffee spread to the Arabian Peninsula, where it became a popular beverage in the Islamic world. It reached Europe in the 17th century and has since become a global commodity.
Cocoa (Cacao)
Origin: Amazon Basin, South America
Historical Context: Cultivated by the Maya and Aztec civilizations for its beans, which were used to make a revered beverage. Cocoa was introduced to Europe in the 16th century, where it became the basis for chocolate.
Sugarcane
Origin: Southeast Asia
Historical Context: Domesticated in New Guinea, sugarcane spread to India and then to the Islamic world. It became a major crop in the Caribbean and the Americas during the colonial period, playing a key role in the transatlantic slave trade.
Banana
Origin: Southeast Asia
Historical Context: One of the oldest cultivated plants, bananas spread to Africa, and their cultivation was established in the Americas by the Portuguese in the 16th century. Today, bananas are a key tropical fruit globally.
Quinoa
Origin: Andes Mountains, South America
Historical Context: Domesticated by the Incas, quinoa was a staple grain in pre-Columbian Andean civilizations. It has gained international popularity in recent years as a superfood.
Grapes
Origin: Near East
Historical Context: Grapes have been cultivated for over 6,000 years, primarily for wine production. Ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all had a rich tradition of viticulture, which spread throughout Europe and beyond.