#Insuline #beta cells #pancreas fatty15, omega36 #cell health #chromium #vanadium #diabetics
Background:
Insulin is essential for allowing glucose and other nutrients to enter cells. If a cell is deprived of glucose despite having glucose in the bloodstream, it may be an indication that insulin is not functioning effectively. This scenario often manifests as high blood glucose levels, observable through a finger test (glucose/sugar level test), even upon waking in the morning without having eaten, known as the dawn phenomenon. At this time your blood sugar level is high.
Concept 1: High Blood Glucose and Cellular Glucose Uptake
High glucose levels in the blood can mean that cells are not receiving the glucose they need. This may occur because the cells do not require glucose at certain times, such as during sleep. At night, not all of the 30 to 50 to 100 trillion cells in the body need glucose, thus the body doesn’t require a high quantity of glucose. It’s important to monitor glucose intake in the evening. Light evening exercise can help consume extra glucose and prevent high glucose levels during rest. ( This opposite is also true, much activity will require much more glucose and then you can get “burn” out and feel low.. when the sugar level gets too low)
If excess glucose circulates while many cells are inactive, liver cells, which remain active at night, will store the surplus glucose. This stored glucose is released early in the morning, typically between 4 to 5 AM, ensuring you wake up feeling not hungry or tired, as the liver releases the stored glucose.
Concept 2: Insulin and Glucose Entry into Cells
If you have normal or elevated blood glucose levels but still feel unwell, it is crucial to determine if glucose is entering your cells efficiently. Insulin is the key that unlocks cell doors to allow glucose in. \ Getting your fasted insulin blood work is critical \ and any other type of measurement for insulin level can act as data to inform the person about their pancreas production of insulin.
Adequate insulin levels are necessary to facilitate this process. If your prescribed medications, such as those starting with “M” or “D,”. Using the M drug you don’t observe effectively managing your condition, using D drug seems to be helping to manage the glucose level much more efficiently.
Mechanism of Action:
The D Drug -Sulfonylureas: These drugs stimulate the beta cells in the pancreas to produce more insulin, directly increasing insulin levels and lowering blood sugar.
- When taken, they can normalize sugar levels, suggesting that insulin production may be the issue.
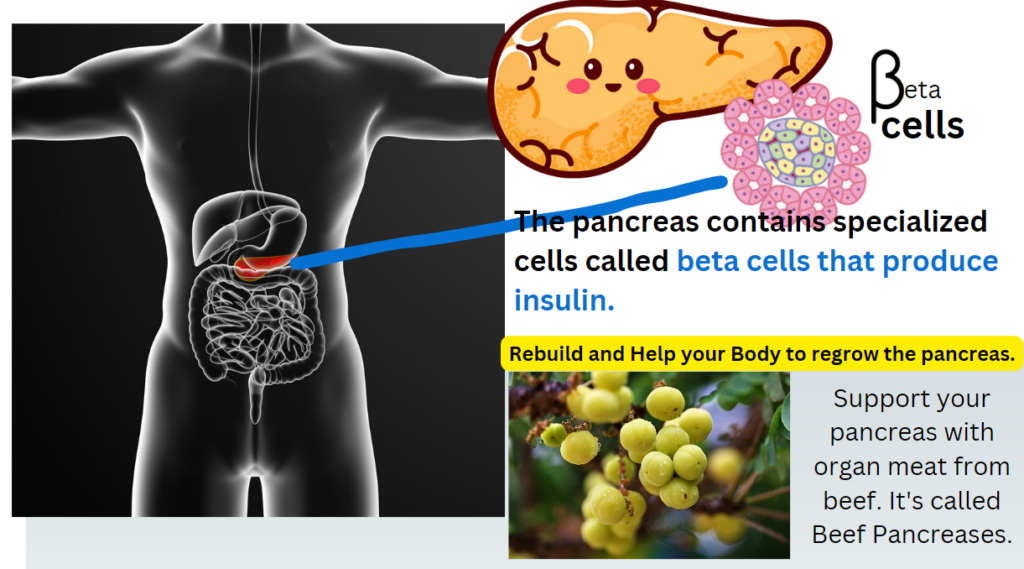
- Consider supporting pancreatic health through diet and supplements. Research indicates that Damsel (Phyllanthus acidus) may improve pancreatic function and restore beta cells:
- Phyllanthus acidus (Damsel) Research
- Eating beef organs, specifically the pancreas, can potentially support human pancreatic function: Beef Pancreas Supplement.
The M drug – Metformin: This medication primarily reduces glucose production by the liver and improves the body’s sensitivity to insulin, rather than increasing insulin production directly.
So you may understand that the M drug does not work or make a difference because its job to stop Liver from releasing the stored glucose. That is ok! But it does not work because you have eaten and when you eat the sugar level get spike, here there is not need for liver to release glucose, because the GUT has sent glucose to the blood directly.
So the focus on the pancreas to crease effective amount of insulin may be the main focus -and this is why it may be important to focus on the pancreas and it beta cells.
Remember to continue to use your medication and consult with your doctor for all changes you wish to make to your life. Your doctor knows best.
However, you need to focus on getting the organs functioning back to normal levels. You will also want to ensure that your cells are getting the right structural nutrients that is the fatty acids: Omega 3, Omega 6 and Fatty Acid (C:15) to ensure that the cells begins to be properly structured with nice membranes that can allow their response to the insulin to be effective.
For Cellular Health the following are required daily nutritional products:
- Cod Liver Oil or Other good Fish Oil Supplement with High Levels of DHA like 1000mg Omega 3 Health EPA/DHA Fish Oil Fatty Acids Capsules 2 Months Supply – BodyHealth.com LLC
- Vanadium and Chromium Trace Minerals https://a.co/d/bmlajZo
- The fatty Acid c15 Fatty 15 supplements: fatty15.com/SFJD33Q9
The research is now on to start looking into pancreases restoration.
Updated: August 4th 2024 – as there is a lack of information on pancreases.
Research into pancreatic restoration focuses on understanding and developing therapies to regenerate or repair pancreatic tissue, particularly the insulin-producing beta cells, which are crucial in managing diabetes. Here are some key areas of ongoing research in pancreatic restoration:
1. Stem Cell Therapy
- Differentiation into Beta Cells: Scientists are working on differentiating stem cells (embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells) into functional beta cells. These beta cells could potentially be transplanted into patients to restore insulin production.
- Regenerative Medicine: The use of stem cells to repair or regenerate damaged pancreatic tissue is a promising area of research. This approach aims to replenish lost or dysfunctional beta cells in conditions such as Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
2. Gene Therapy
- Gene Editing: Technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 are being explored to correct genetic defects that may cause beta cell dysfunction or death. Gene therapy could also be used to modify other cell types in the pancreas to become insulin-producing cells.
- Regulation of Gene Expression: Research is focused on understanding and manipulating the genes that control beta cell proliferation and function to enhance beta cell regeneration.
3. Immunotherapy
- Immune Modulation: For Type 1 diabetes, where the immune system attacks beta cells, immunotherapy aims to protect or restore these cells by modulating the immune response. This includes using monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, or immune-modulating drugs to prevent autoimmune destruction.
- Tolerogenic Vaccines: Developing vaccines that induce immune tolerance to beta cells, potentially preventing the immune system from attacking them.
4. Bioengineering and Islet Transplantation
- Islet Transplantation: Transplanting islets (clusters of insulin-producing cells) from a donor pancreas into a diabetic patient is a therapy under investigation. This method faces challenges such as immune rejection and the shortage of donor organs.
- Encapsulation Technologies: Encapsulating transplanted beta cells or islets in a semi-permeable membrane can protect them from immune attack while allowing insulin to be released. This approach aims to prolong the survival and function of transplanted cells.
5. Pharmacological Approaches
- Beta Cell Proliferation: Research is being conducted on drugs that can stimulate the proliferation of existing beta cells. Small molecules and growth factors that promote beta cell growth and survival are being explored.
- Beta Cell Neogenesis: Identifying factors that can induce the formation of new beta cells from progenitor cells within the pancreas is another area of focus.
6. Regenerative Factors and Signals
- Understanding Beta Cell Regeneration: Studies aim to understand the signals and pathways that regulate beta cell regeneration. This includes research into the role of various hormones, cytokines, and growth factors.
- Role of the Pancreatic Microenvironment: Investigating how the pancreatic microenvironment influences beta cell survival and function is crucial. This includes understanding the role of other cell types in the pancreas and the extracellular matrix.
7. Artificial Pancreas
- Closed-Loop Systems: Research into artificial pancreas systems, which combine continuous glucose monitoring with automated insulin delivery, is ongoing. While not a direct restoration of pancreatic function, these systems aim to better mimic the glucose regulation performed by a healthy pancreas.
8. Lifestyle and Nutritional Interventions
- Diet and Exercise: Research also explores how lifestyle interventions can preserve beta cell function and delay the progression of diabetes. This includes studying the impact of specific diets, exercise, and weight management.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Overcoming Immune Rejection: Developing methods to protect transplanted or regenerated beta cells from immune attack is a significant challenge.
- Long-term Functionality: Ensuring the long-term viability and functionality of regenerated or transplanted beta cells is crucial for successful treatment.
- Safety and Efficacy: Ensuring that new treatments are safe and effective is a primary concern, especially with advanced therapies like gene editing and stem cell treatments.
The field of pancreatic restoration research is rapidly evolving, with significant progress being made toward developing effective therapies for diabetes and other pancreatic disorders. Collaboration between scientists, clinicians, and biotechnology companies is essential to translating these research findings into clinical applications.